Developing with Fleetbase Webhooks
Webhooks in Fleetbase provide a powerful way to integrate real-time event-driven functionalities into your external applications or services. By setting up webhooks, your system can instantly react to various events occurring within the Fleetbase platform.
Setting Up Webhooks
Fleetbase provides an easy to use interface for creating and monitoring webhook events.
Creating a Webhook
-
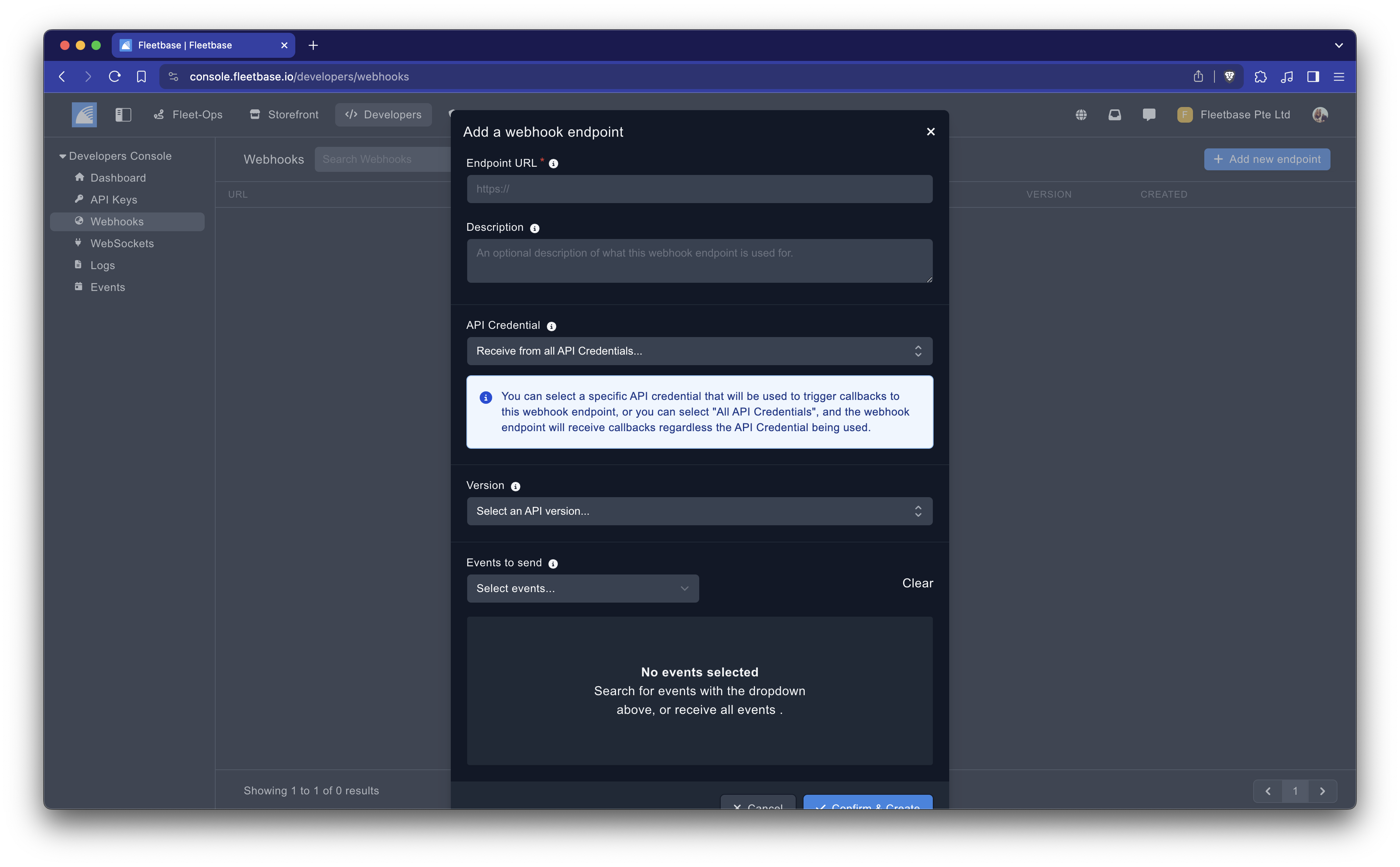
Navigate to the Developers Section: Access the Fleetbase console and go to the Developers section, then select the Webhooks option.
-
Specify the Receiving Endpoint: Enter the URL of the endpoint where you want Fleetbase to send webhook events. This endpoint should be a server you control which is capable of receiving HTTPS POST requests.
-
Select Events: Choose the specific events you wish to receive notifications for. You can subscribe to individual events related to resources like orders, drivers, or vehicles, or opt to receive all available events.
Configuring Your Endpoint
Ensure that your endpoint is set up to:
- Accept HTTPS POST requests.
- Validate incoming requests to ensure they are coming from Fleetbase.
- Respond correctly to HTTP challenges (if applicable) to verify ownership of the endpoint.
Practical Uses of Webhooks
Webhooks can be utilized in various scenarios such as:
- Order Updates: Receive real-time notifications when orders are created, updated, or status changes.
- Driver Monitoring: Get alerts when a driver starts a route, completes a delivery, or updates their status.
- Inventory Management: Automatically update inventory levels in your ERP or inventory management system when sales or returns occur.
Testing Your Webhooks
Manual Testing
-
Send Test Event: From the webhook configuration page in the Fleetbase console, use the functionality to send a test event to your endpoint.
-
Check Your Endpoint: Ensure that your server logs the incoming requests. Verify that the payload and headers are received as expected.
Automated Testing
Set up automated tests that simulate webhook calls using tools like Postman or curl. For example:
curl -X POST https://your-endpoint.com/webhook -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"event":"order.updated","data":{"id":"order_xxxabc","status":"dispatched"}}'
Processing Incoming Data
An example of receiving a Fleetbase in a Laravel application.
<?php
use Illuminate\Routing\Controller;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use DriverManagement;
class WebhookReceiverController extends Controller {
public function handler(Request $request) {
$event = $request->input('event');
$data = $request->input('data');
if ($event === 'driver.location_changed') {
$location = $data['location'];
try {
DriverManagement::updateLocation($data['id'], $location);
} catch (\Throwable $e) {
return response()->json(['error' => $e->getMessage()], 400);
}
}
}
}
The incoming webhook data will be structured like so:
{
"id": "<the event id>",
"api_version": "<the api version>",
"event": "<the event name>",
"created_at": "<the event datetime>",
"data": {
"id": "<the resource id>",
...other attributes
"additionalData": {}
}
}
The data will typically be the updated properties of the resource subscribed to, the event will name the type of event. For example it could be driver.location_changed or driver.updated.
Common Webhook Development Practices
Security Practices
- Validate Payloads: Always verify that the incoming data is from Fleetbase using signatures or comparing the IP address against known Fleetbase IPs.
- Use HTTPS: Ensure that your endpoint is secured with HTTPS to protect the data transmitted between Fleetbase and your server.
Error Handling
- Responding to Failures: Make sure to handle failures gracefully. If your endpoint encounters an error, it should log this error and respond with appropriate HTTP status codes.
- Retries: Understand Fleetbase's retry mechanism. Ensure your system can handle or ignore duplicate events in case of delivery retries.
Scalability
- Asynchronous Processing: Consider processing the webhook payloads asynchronously if the processing is resource-intensive, to quickly respond to incoming webhook calls.
Viewing Webhook Logs
Fleetbase provides logging for each webhook event sent. You can view these logs in the console under the Webhooks section. This is useful for:
- Debugging: Quickly identifying and resolving issues related to event handling.
- Audit Trails: Keeping track of what events were sent and when, including the payload and the response received by Fleetbase.
Conclusion
Webhooks are a crucial feature for developing responsive and integrated logistic systems with Fleetbase. By following this guide, you can set up, test, and effectively use webhooks to enhance the capabilities of your applications, ensuring they remain synced with real-time data and events from Fleetbase.